What is Net Interest Income?
Net Interest Income (NII) is a profit metric equal to the difference between a bank’s total interest income and the interest expense incurred.

How to Calculate Net Interest Income
The net interest income is the earnings generated by a company’s interest-bearing assets, subtracted from its interest-bearing liabilities.
The net interest income, frequently abbreviated as “NII”, is a measure of profitability most often used within the financial sector.
For example, the NII metric is one method to analyze the margin profile of commercial banks, corporate banks, and institutional lenders.
The net interest income calculation requires subtracting a company’s interest expense from its interest income.
- Interest Income → The interest earned by the bank’s outstanding loan portfolio (“cash inflow”).
- Interest Expense → The interest paid by the bank on outstanding customer deposits (“cash outflow”).
Net Interest Income Formula
The formula for calculating net interest income is the difference between the interest income and interest expense.
The business model of a bank lender is based on structuring loans to individuals or corporate borrowers in exchange for periodic interest payments until the date of maturity.
At maturity, the borrower is obligated to return the original principal amount to the lender, including all accumulated interest, if applicable – i.e. paid-in-kind interest (PIK).
Within a lending portfolio, the interest-earning assets consist of mostly loans, mortgages, and other financing products.
On the other hand, the bank’s interest-bearing liabilities consist of customer deposits and borrowings from other banks.
What is a Good Net Interest Income?
Like most profit metrics, comparisons to industry peers are not feasible without standardizing the metric beforehand.
The profitability of a bank lender can be compared to that of its industry peers via the net interest margin (NIM).
The formula to calculate the net interest margin (NIM) is the net interest income of a bank divided by the average loan portfolio value.
Net Interest Income Calculator
We’ll now move to a modeling exercise, which you can access by filling out the form below.
Step 1: Loan Portfolio Assumptions
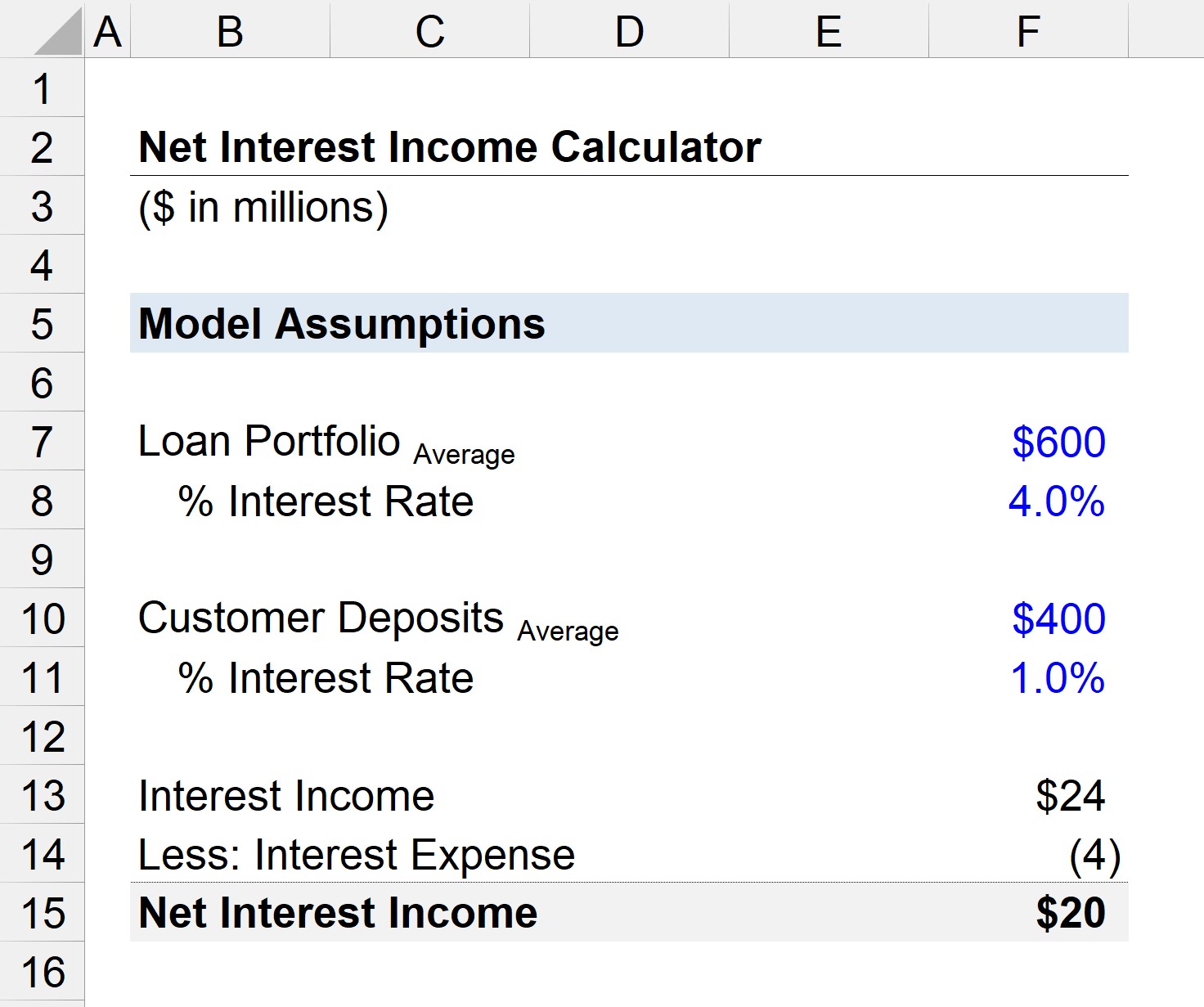
Suppose we have a corporate bank with an average outstanding loan portfolio amounting to $600 million.
The average loan is calculated as the sum of the beginning and end-of-period values of the bank’s outstanding loans, divided by two.
The average interest rate on loans will be assumed as 4.0% for purposes of simplicity.
- Loan Portfolio = $600 million
- Interest Rate = 4.0%
As for the customer deposits at the bank, the average value is $200 million, and the applicable interest rate is 1.0%.
- Average Customer Deposits = $400 million
- Interest Rate = 1.0%
Step 2: Net Interest Income Calculation Example
Using those assumptions, we can calculate the corporate bank’s interest income as $24 million and its interest expense as $4 million.
- Interest Income = $600 million × 4.0% = $24 million
- Interest Expense = ($400 million) × 1.0% = ($4 million)
In conclusion, the difference between the bank’s interest income and interest expense is $20 million, which represents its net interest income for the current year.
- Net Interest Income (NII) = $24 million – $4 million = $20 million

Everything You Need To Master Financial Modeling
Enroll in The Premium Package: Learn Financial Statement Modeling, DCF, M&A, LBO and Comps. The same training program used at top investment banks.
Enroll Today






You have the following information about a bank’s loan portfolio:
Size of portfolio: USD 1 billion
Gross interest rate: 7%
Cost of funds: 5.25%
Expected loss (EL): 1.4%
What is the bank’s forecast net income?
Hi, Andy,
The gross interest income would be 7% of the 1bn portfolio, but the interest expense would depend on the amount of the portfolio that was funded by interest-bearing liabilities * the cost of those liabilities.
BB